
Orlando Web Design & Development
1. Website Organization & Structure:
A server is like a house because both store lots of things or information. In a house rooms help us keep everything organized, while in a server information is organized in directories.
For example, think about your room. In your room, you have lots of different furniture and each piece has a purpose. On your desk you might have your computer, books and office supplies. You can use a chest to store your clothes and on your nightstand you might keep your iPod & cellphone.
On a server directory you can store a website. Instead of furniture, the server uses sub-directories to store and organize all the media files (images, audio files, video, PDF’s, etc.) that belong to that website.
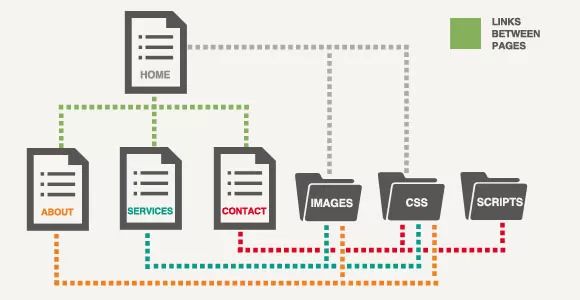
When you create websites you must always keep all the files organized by relevant sub-directories. It’s also important that you keep everything that belongs to a website together otherwise your links, images and scripts will not work.
A simple website structure looks like this:
2. HTML5 Structure
A simple HTML5 website uses the following semantic/structural elements:
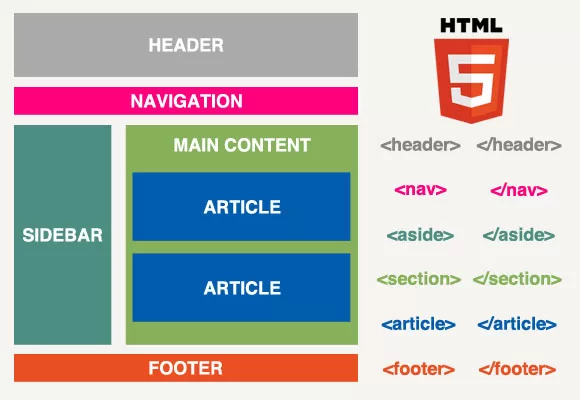
- <header> </header> Defines a header for a document or section
- <nav> </nav> Defines navigation links
- <aside> </aside> Defines content aside from the page content
Aside should only be used if its content is related to the content around the aside - <section> </section> Defines a section in a document
- <article> </article> Defines an article
- <footer> </footer> Defines a footer for a document or section
3. Creating Links
The HTML <a> tag defines a hyperlink. A hyperlink (or link) can be a word, group of words, or an image.
a. Tips To Create Effective Links:
- Do not use “click here”
- Use descriptive words, so users can know where they are going after they click.
- If you are linking to a file, give the file format and size.
- Do not use blank spaces. They render in the browser as %20.
b. Relative Links Vs. Absolute Links
Relative links are links within the website directory. Relative links do not need to include the http protocol or the website’s domain name.
Example:
<a href="mypage.html">My Page</a>
Absolute links are links that go to other websites. Absolute links require the full URL (protocol, domain name, directory name and file name.
Example:
<a href="http://www.google.com/">Link to Google</a>
Always have absolute links open in a new page by adding the target attribute “_blank”. The target attribute specifies where to open the linked document.
Example:
<a href="http://www.google.com/" target="_blank">Link to Google</a>
c. Linking To A PDF File
To link to a file within the website’s directory add the file path to the hyperlink reference and use “_blank” for the target attribute. Don’t forget to specify the file type and file size.
<a href="downloads/lesson2.pdf" target="_blank">Download Lesson 2 (PDF 94 KB)</a>
d. Linking Within A Page
You can create links within a page using ID’s.
1. Give an ID to the section you want to link to
<p id="bio">My Bio</p>
2. Create the link to go to the ID. Please note that a pound sign must go before the ID name.
<a href="#bio">My Bio</a>
e. Tooltips
A tooltip is a message that displays when when the mouse hovers above a link. To create a tooltip add the title attribute to the <a> tag.
Example:
<a href="bio.html" title="learn more about me">My Bio</a>
f. Linking To An Email
To Link to an email use “mailto” on the hyperlink reference.
Example:
<a href="mailto:martha@gmail.com">martha@gmail.com</a>
4. Inserting An Image
The <img> tag defines an image in an HTML page. The <img> tag has two required attributes: src and alt. The alt specifies an alternate text for an image.
<img src="images/my-image.png" alt="Description about my image" />
The HTML tag <figure> specifies self-contained content, like illustrations, diagrams, photos, code listings, etc. If the image has a caption, you can use the tag <figcaption> to add a description.
<figure> <img src="images/my-image.png" alt="Description about my image" /> <figcaption> This is the description of my image</figcaption> </figure>
5. Linking An Image
<a href="http://www.website.com/" target="_blank"> <img src="images/my-image.png" alt="Description about my image" /></a>
6. Using HTML Special Characters
Entities are used to implement reserved characters or to express characters that cannot easily be entered with the keyboard.
ampersand & & copyright © © registered trademark ® ® trademark ™ ™ Quotes " " Accents à à Non Breaking Space
HTML can render mathematical symbols, Greek characters, various arrows, technical symbols and shapes.
« « ♠ ♠ ♦ ♦ » » ♣ ♣ → → • • ♥ ♥
Please Note: Entity names are case sensitive.






